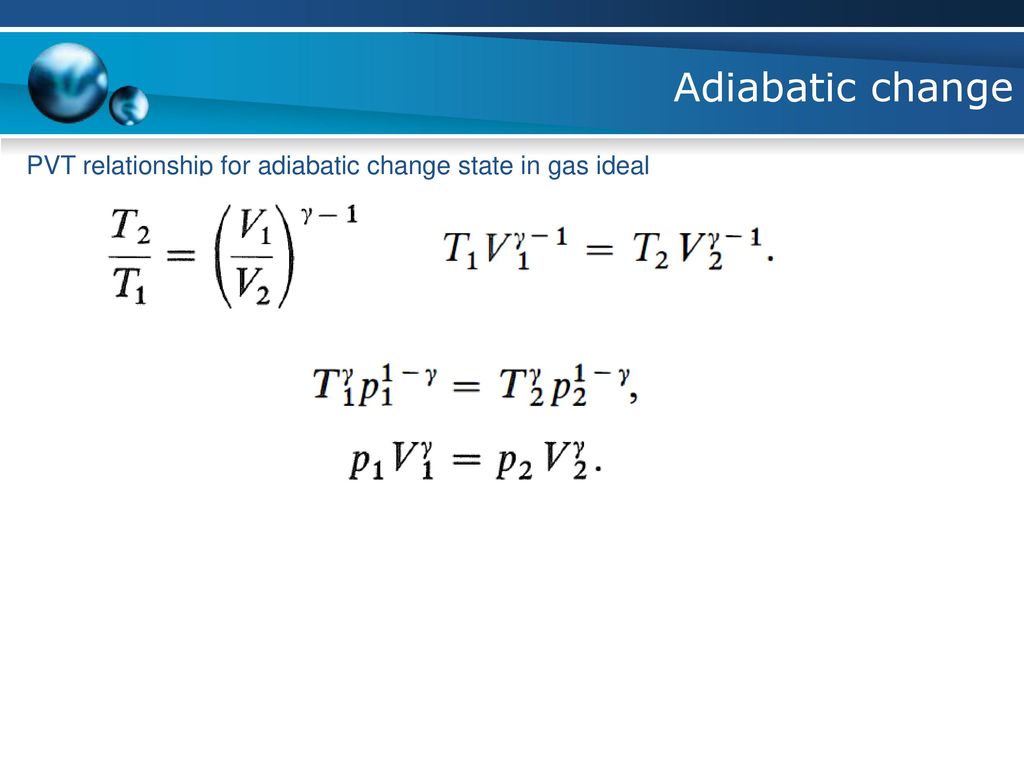
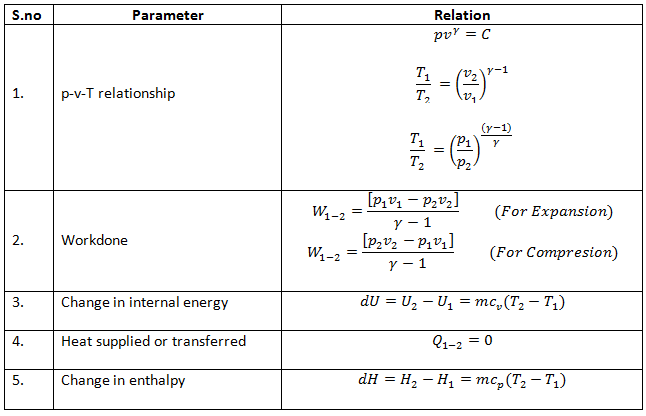
Pvt relation for adiabatic process 211793-Pvt relation for adiabatic process
Feb 28, 08 · The relationship between pressure and volume of an ideal gas is expressed as pv=constant in a reversable isothermal condition Show that the relationship between pressure and volume of the same gas is expressed as pV^gamma=constant in a reversible adiabatic condition where gamma=Cp,m/Cv,m Homework Equations gamma=Cp,m/Cv,mMay 22, · Adiabatic Relation Between V and T For one mole of gas, PV= RT P =RT/V Putting PV r =G, we get RT/V * V r = G or T*V (r 1) = G/ R = TV (r 1) = G (Constant) This equation describes the adiabatic relation between V and T for an ideal gas Adiabatic Reversible and Irreversible process Reversible Adiabatic ProcessSep 10, · No headers For an ideal gas in an isothermal process, PV = constant In a reversible adiabatic process PV γ = constant, TV γ − 1 = constant, P 1 − γ T γ = constant From these it is easy to see that the ratios of the adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric slopes are as follows

Mman2700 Formula Sheet Mman2700 Thermodynamics Formula Sheet 1 Properties Of Ideal Gases P V Mrt Pv Rt P1 V1 P2 V2 T1 T2 U2 U1 Cv T2 T1 H2 H1 Course Hero
Pvt relation for adiabatic process
Pvt relation for adiabatic process-Jun 13, 16 · One of the good applications of the adiabatic process The pendulum oscillating in a vertical plane is an example of it A quantum harmonic oscillator is also an example of an adiabatic system When we put the ice into the icebox, no heat goes out and no heat comes inMay 11, 15 · 2CONSTANT PRESSURE PROCESS • An isobaric process is a thermodynamic process in which the pressure stays constant ΔP = 0 • The term derives from the Greek iso (equal) and baros (weight) The heat transferred to the system does work, but also changes the internal energy of the system
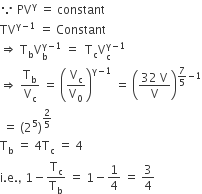


A Diatomic Ideal Gas Is Used In A Carnot Engine As The Working Substance If During The Adiabatic Expansion Part Of The Cycle The Volume Of The Gas Increases From V To
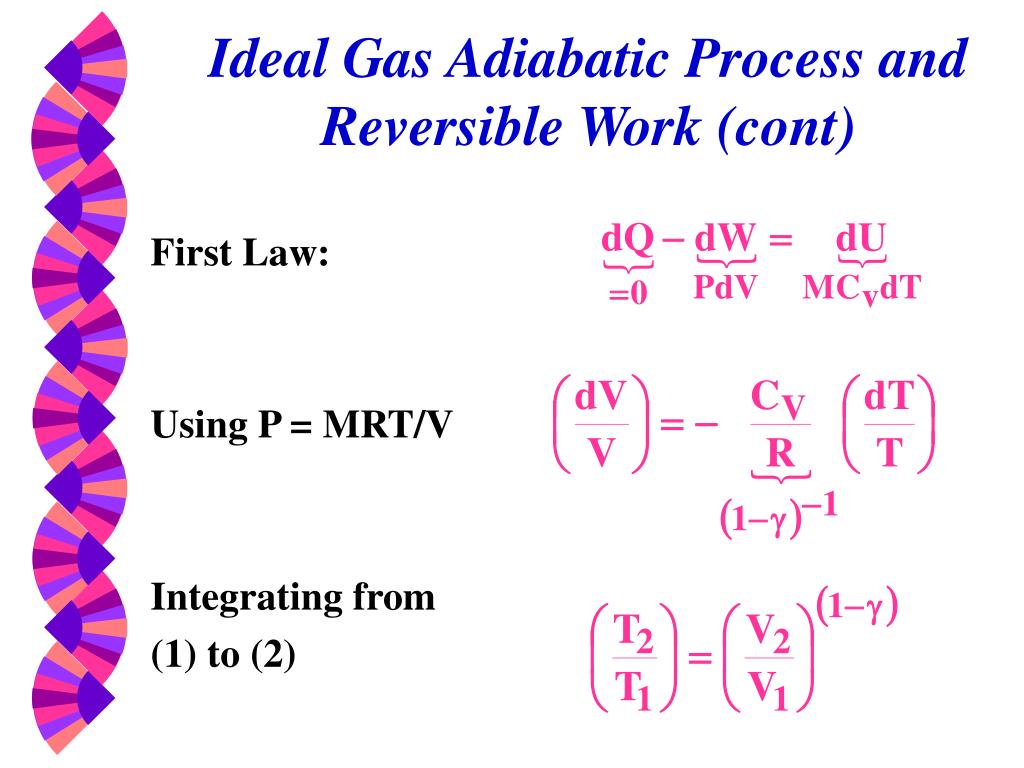
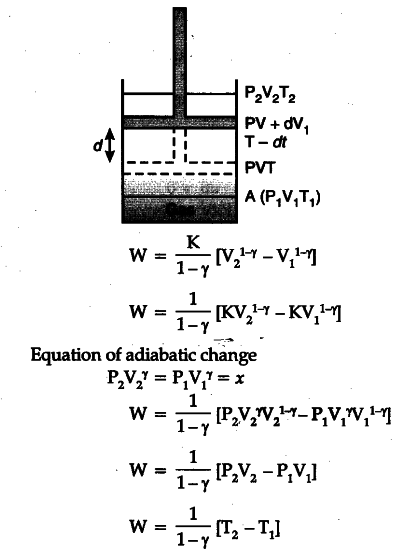
Sep 10, · No headers An adiabatic process is one in which no heat enters or leaves the system, and hence, for a reversible adiabatic process the first law takes the form dU = − PdVBut from equation 811, C V = (∂U/∂T) VBut the internal energy of an ideal gas depends only on the temperature and is independent of the volume (because there are no intermolecular forces), andAdiabatic Process An adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process, in which there is no heat transfer into or out of the system (Q = 0) The system can be considered to be perfectly insulatedIn an adiabatic process, energy is transferred only as work The assumption of no heat transfer is very important, since we can use the adiabatic approximation only in very rapid processesDec 14, 18 · in this video derive an expression for PVT relation of adiabatic process or isentropic process
Jun 19, 16 · In my text book of Physics, first they give the equation for adiabatic process using the first law of Thermodynamics, as;Sep 09, 18 · The equation of state for an adiabatic process is given by Here γ is called adiabatic exponent (γ = C p /C v) which depends on the nature of the gas The equation (5) implies that if the gas goes from an equilibrium state (P i,V i) to another equilibrium state (P f ,V f) adiabatically then it satisfies the relation The PV diagram of anView 3_PVT Relationspptx from SCIENCES CHEMISTRY 12CHY455 at Amrita School of Engineering PVT Relations (Pure Substances) Dr Udaya Bhaskar Reddy Ragula Assistant Professor (SG) Department of
Processes, Adiabatic Process, PVT Relationship, PV diagram, TS diagram, Change in Internal Energy, Change in Entropy, Work done, Heat Transferred, Constant Temperature Process, PVT Relationship, PV diagram, TS diagram, Change in Internal Energy, Change in Entropy, WorkAug 10, · As noted above, in an adiabatic process \(\Delta U = w_{ad}\) so that \w_{ad} = C_V \, \Delta T \label {252}\ This relationship makes sense because the energy needed to carry out the work of the expansion must come from the gas particles, which will lose energy as they do work, resulting in a drop in the temperature of the systemWe assumeNote that dU = m C V dT, C V = (R/MW)/ ( g 1), PV = nRT and dW = P dV You will arrive at the form



Derivation Pv Gamma Youtube



Understanding Advanced Thermodynamics For Gate And Ies Aspirants By Harshit Aggarwal Unacademy Plus
Sep 19, 11 · The key difference between adiabatic and polytropic processes is that in adiabatic processes no heat transfer occurs whereas in polytropic processes heat transfer occurs In chemistry, we divide the universe into two parts The part we are going to study is "a system", and the rest is "the surrounding"D E int = W → (1) where, ΔE int ⇒ change in internal energy and W ⇒ workdone Then, they used the relation C v = Q / n d tDec 03, 10 · Relation between PVT Adiabatic process Polytropic process Constant Volume Process Throttling Process Assumptions in Thermodynamic Cycles The analysis of all thermodynamics cycles is based on the following assumptions 1 The gas in



Adiabatic Process P V T Relation Youtube


7 5 Partial Derivatives With Respect To T P And V Chemistry Libretexts
The Dry Adiabatic Lapse Rate We will now derive an expression for the rate of change of temperature with height of a parcel of dry air as it moves about in the Earth's atmosphere Since the air parcel undergoes only adiabatic transformations (dq = 0), and the atmosphere is in hydrostatic equilibrium, for a unit mass of air in the parcel weGeneral representation of adiabatic process is mathPV^\gamma/math= constant In most general cases under Thermodynamics, math\gamma=14/math In some casesOne for constant pressure (cp) and one for constant volume (cv) Note that, this ratio κ = cp/cv is a factor in determining the speed of sound in a gas and other adiabatic processes Other p, V, T Relation On a pV diagram, the process occurs along a line (called an adiabat) that has the equation p = constant / Vκ



Jee Main 19 Physics Solutions A Rigid Diatomic Ideal Gas Undergoes An Adiabatic Process At Youtube
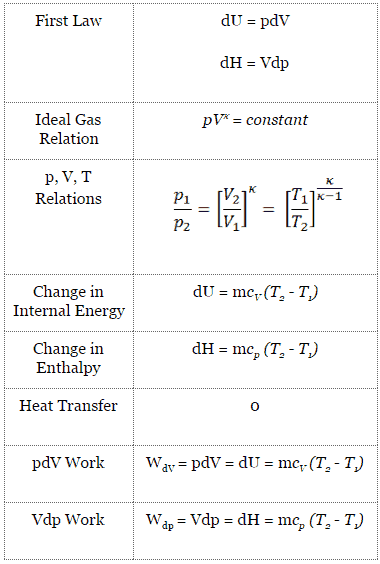


What Is Adiabatic Process Definition
Derivation of the relation between temperature and pressure for an irreversible adiabatic expansion I have a formula for finding the final temperature in an irreversible adiabatic expansion T2 = CV P2 P1 CpT1, where T1 is the initial temperature CV and Cp are the molar heat capacities at constant volume and constant pressure, respectivelyThermodynamic Processes and Equations!Ie, no heat is transferred A rapid expansion or contraction of a gas is very nearly adiabatic Any process that occurs within a container that
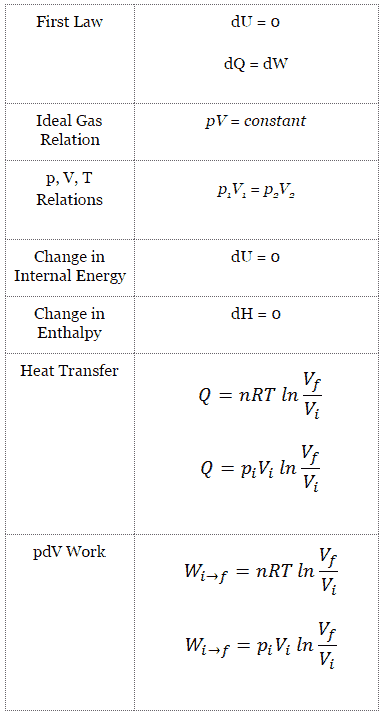


What Is Isothermal Process Definition



How To Derive Adiabatic Process
Adiabatic Process An adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process, in which there is no heat transfer into or out of the system (Q = 0) The system can be considered to be perfectly insulatedIn an adiabatic process, energy is transferred only as work The assumption of no heat transfer is very important, since we can use the adiabatic approximation only in very rapid processesIsentropic Process and the First Law The first law of thermodynamics in terms of enthalpy dH = dQ Vdp or dH = TdS Vdp See also First Law of Thermodynamics See also Ideal Gas Law See also What is Enthalpy In this equation the term Vdp is a flow process workThis work, Vdp, is used for open flow systems like a turbine or a pump in which there is a "dp", ie change in pressureFeb 23, 13 · Start with the first law of thermodynamics dQ = dU dW (remember that the d's on Q and W are "inexact differentials", if you really care at all) By definition, there is no heat transfer in an adiabatic process Thus, any infinitesimal heat transfer, dQ, is zero Thus 0 = dU dW



35 Minute D Question 8 10 Pts The Relation Pv Nrt Holds For All Ideal Gases
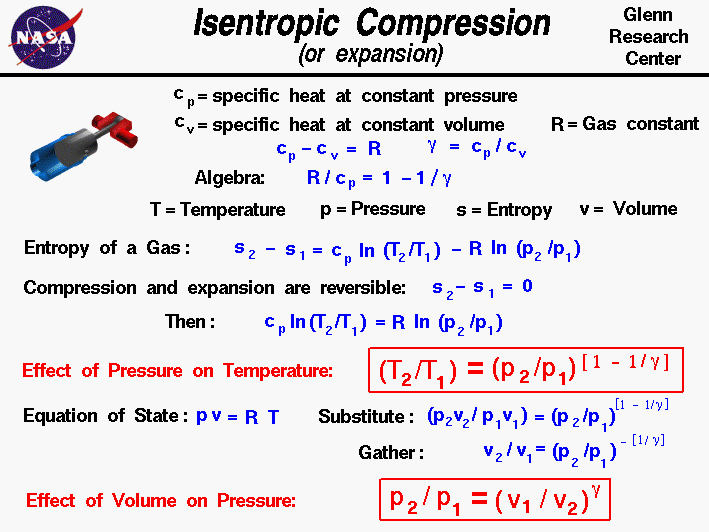


Isentropic Compression Or Expansion
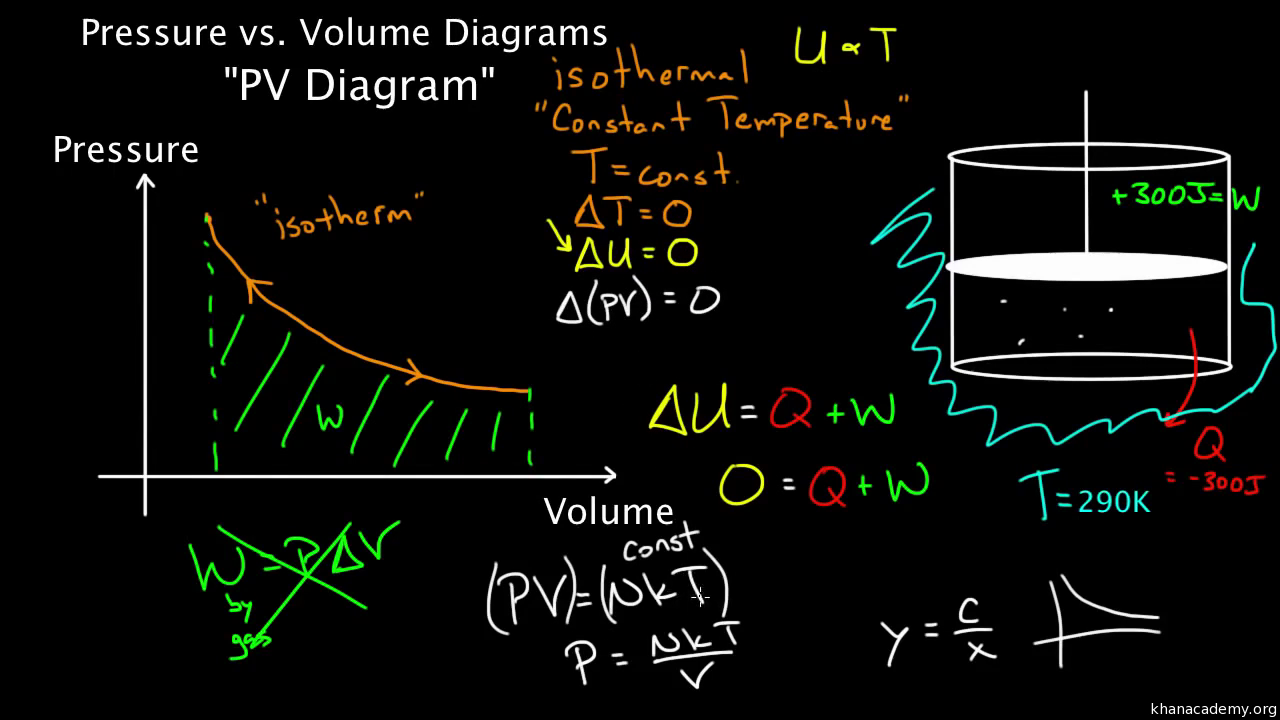
This is usually called the isothermal gas law Suppose, now, that the gas is thermally isolated from its surroundings If the gas is allowed to expand quasistatically under these so called adiabatic conditions then it does work on its environment, and, hence, its internal energy is reduced, and its temperature changes Let us work out the relationship between the pressure and volume of theProof of Pressure, Volume and Temperature Ratio Proof, in this tutorial you will learn about one of the most important relation to solve Numerical problems iDec 31, 19 · Since, assuming an adiabatic system, the pressure is directly related to the volume and thus to the density In this way the barometric formula can also be formulated for the density For an adiabatic process, pressure and volume of two states are related to each other by the following equation \begin{align}
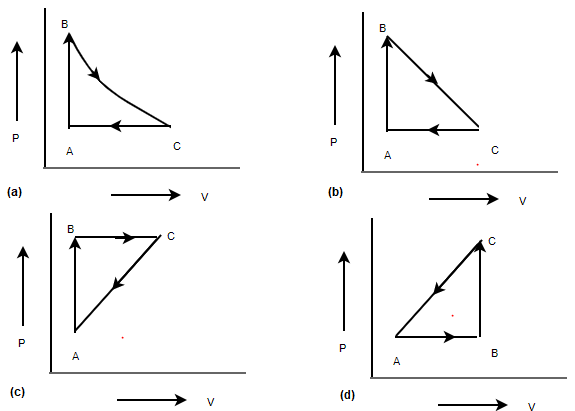


P V Diagram Problems And Solutions



Thermodynamic Properties W Property Table From Direct Measurement
During the adiabatic change of ideal gas, The relation between the pressure and the density will be A P 2 p 1 d 1 − γ = p 2 d 2 − γ For an adiabatic process, P 1Vapor compression cycle CARNOT CYCLE • Was introduced by Nicolas Sadi Carnot • The most efficient thermodynamic cycle • Is composed of four basic processes isothermal heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion, isothermal rejection ofOct 21, 17 · Process 01 Suction process In this process, the inlet valve opens and suction of air takes place at atmospheric pressure It is called as suction stroke Process 12 Isentropic Compression The air sucked is now compressed isentropically Due to the compression, the temperature of the air increases to such level at which the diesel gets



Why Is Pv Gamma Constant In An Adiabatic Process Physics Stack Exchange



Is The Relation P V Gamma Constant Not Valid For Irreversible Adiabatic Process Quora
Dec 22, 17 · Adiabatic means constant heat energy, and it can be used to name a thermodynamic process or a system where adiabatic process is taking place Adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process that occurs without any heat transfer between a system and its surrounding Here, either heat or matter is not transferred into or out of the systemAug 24, 01 · Ideal Bose equation of state The equation of state for an ideal Bose gas is p V m = R T Li α 1 ( z ) ζ ( α ) ( T T c ) α {\displaystyle pV_ {m}=RT~ {\frac { {\text {Li}}_ {\alpha 1} (z)} {\zeta (\alpha )}}\left ( {\frac {T} {T_ {c}}}\right)^ {\alpha }}The ratio of the specific heats γ = C P /C V is a factor in determining the speed of sound in a gas and other adiabatic processes as well as this application to heat engines This ratio γ = 166 for an ideal monoatomic gas and γ = 14 for air, which is predominantly a diatomic gas


Thermodynamics Ebook Isentropic Process



Solved Lab Experiment 4 Thermodynamics Pdf Page 4 Of 1 Chegg Com
Adiabatic Process So far, we have covered constant volume (isochoric) and constant pressure (isobaric) processes There is a third process that is very important in the atmosphere—the adiabatic processAdiabatic means no energy exchange between the air parcel and its environment Q = 0Note adiabatic is not the same as isothermal(2) During adiabatic compression, the temperature of the system does change Starting from the first law of thermodynamics $$\mathrm{d}U = \mathrm{d}Q \mathrm{d}W$$ For an adiabatic process $\mathrm{d}Q=0$A process is a change in the state of a gas as a result of flow of energy During this flow a change takes place in properties of the substance such as pressure, volume, temperature and also the energy quantities such as



Solved Show That For Adiabatic Processes The Relation Bet Chegg Com



Adiabatic Process And Applications Of Adiabatic Process Iit Jee And Neet Physics
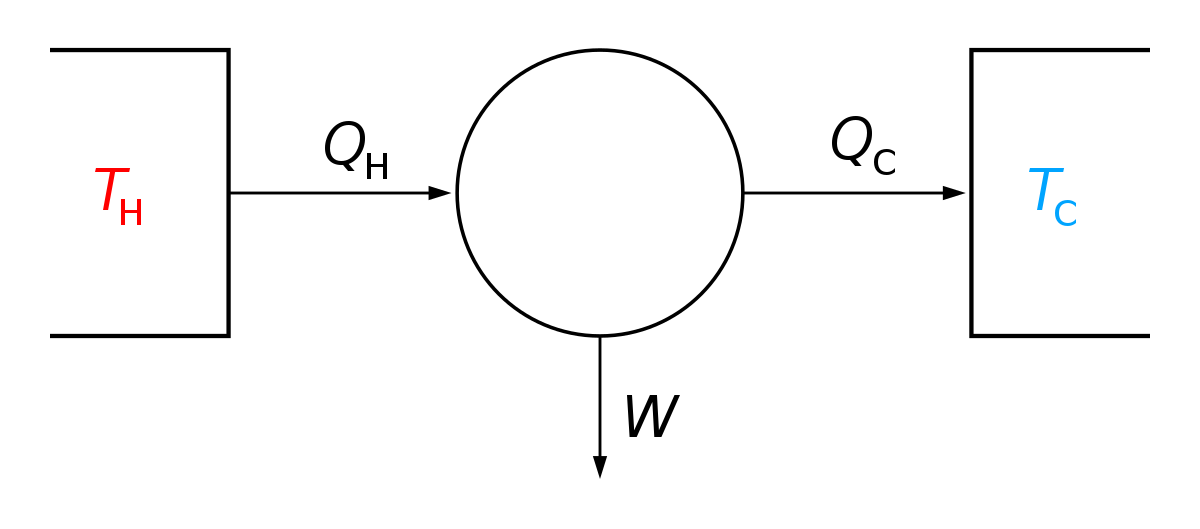
• the gas undergoes an isentropic process → reversible adiabatic Combining this result with the ideal gas equation of state T 2 T 1 = v 1 v 2 k−1 = P 2 P 1 (k−1)/k The isentropic process is a special case of a more general process known as a polytropic process where → Pvn = constant and n is any number Special Cases n =1 Pv= RT = constant ⇒ isothermal processAdiabatic Expansion (DQ = 0) Occurs if • change is made sufficiently quickly • and/or with good thermal isolation Governing formula PV g = constant where g = CP/CV Because PV/T is constant (ideal gas) V g1 T = constant (for adiabatic) P V Adiabat IsothermsAdiabatic process, in thermodynamics, change occurring within a system as a result of transfer of energy to or from the system in the form of work only;



Adiabatic Process Definition Examples Diagrams


What Is Polytropic Process Quora
Adiabatic means process without transfer of heat or matter to surrounding If you know the universal gas law then you might know pressure is inversely proportional to volume and directly proportional to the temperature Imagine a gas is pressuriseSolution Here, the process is adiabatic compression The volume is given and temperature is to be found we can use the equation (8 ) TiViγ1 = TfVfγ1 Ti = 300 K (°C = 300 K) T2 ≈ 522 K or 2490C This temperature is higher than the boiling point of waterAn adiabatic process is a reversible constant entropy process for an ideal gas without heat transfer, following the relationship Pvk = constant A polytropic process is a reversible process for an ideal gas with heat transfer, and variable entropy, following the relationship Pvn = constant
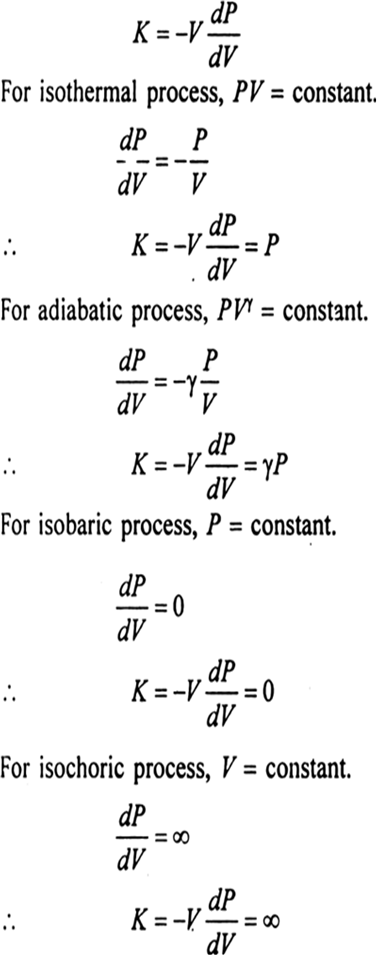


Define Bulk Modulus Find The Bulk Modulus Of Gas For Isothermal Adiabatic Isobaric And Isochoric Processes From Physics Thermodynamics Class 11 Cbse



Adiabatic Process And Applications Of Adiabatic Process Iit Jee And Neet Physics
Since a reversible adiabatic process is necessary for an isentropic process, let™s see what kind of relationship between properties of state will be obtained from the 1law of thermodynamics du=qw where 1 adiabatic fiq=0 2 reversible fiw=pd The 1law of thermodynamics for an isentropic process is now du=pd (1)Browse other questions tagged homeworkandexercises idealgas adiabatic or ask your own question Featured on Meta Stack Overflow for Teams is now free for up to 50 users, forever25 Adiabatic Processes The Path of Least Resistance Adiabatic Process So far, we have covered constant volume (isochoric) and constant pressure (isobaric) processesThere is a third process that is very important in the atmosphere—the adiabatic processAdiabatic means no energy exchange between the air parcel and its environment Q = 0Note adiabatic is not the
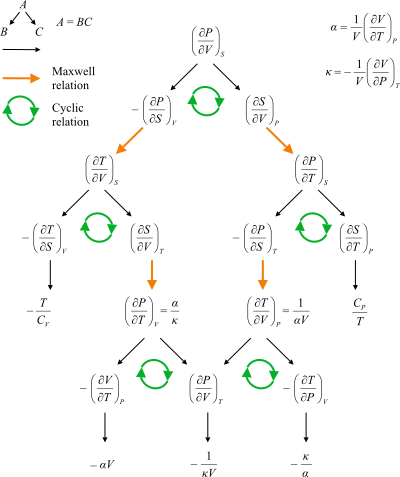


Maxwell Relations Wikipedia


Adiabatic Processes
As per thermodynamic terminology, in adiabatic process, there is no exchange of heat from system to its surroundings neither during expansion nor during compression Whereas in isothermal process, the temperature remains constant throughout the work Understand the difference between isothermal and adiabatic processThe turbine is an example of the adiabatic process as it uses the heat a source to produce work Adiabatic process derivation The adiabatic process can be derived from the first law of thermodynamics relating to the change in internal energy dU to the work dW done by the system and the heat dQ added to it dU=dQdW dQ=0 by definition



Adiabatic Process Relation Between P V And T Testbook



What Is Adiabatic Process Definition


Physical Chemistry I Tkk 2246 Ppt Download


Adiabatic Process Wikipedia


Adiabatic Processes


How To Prove Math Pv Gamma Text Constant Math For An Adiabatic Process Quora



13 Thermodynamics Proof Of Adiabatic Equation Most Important Complete Concept Youtube
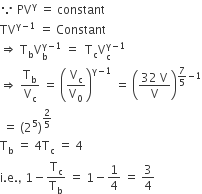


A Diatomic Ideal Gas Is Used In A Carnot Engine As The Working Substance If During The Adiabatic Expansion Part Of The Cycle The Volume Of The Gas Increases From V To


Ppt Thermodynamic Properties Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5036



Neet Test Series Gases Enthalpy
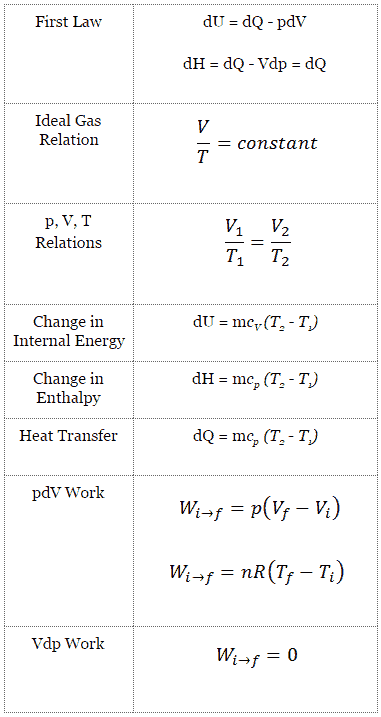


What Is Isobaric Process Definition
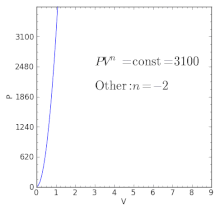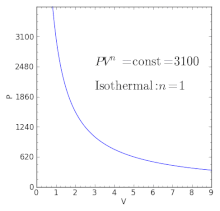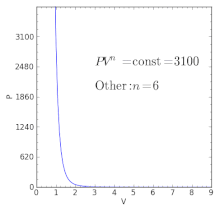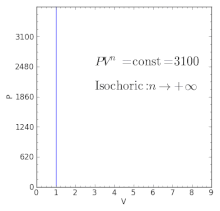


Polytropic Process Wikipedia



Chapter 3c The First Law Closed Systems Diesel Cycle Engines Updated 3 19 13



Certain Perfect Gas Is Found To Obey The Law Pv 3 2 Constant



Ch18 Ssm


Derive An Expression For Work Done In Adiabatic Expansion Cbse Class 11 Physics Learn Cbse Forum


Which Of The Following Relations Does Not Give The Equation Of An Adiabatic Process Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community


What Is Adiabatic Process Explanation Mechanical Booster



Adiabatic Process Definition Examples Diagrams



Chapter 3d The First Law Closed Systems Otto Cycle Engines Updated 4 22 12



Thermodynamic Properties Property Table W Property Table From Direct Measurement W Equation Of State W Equation Of State Any Equations That Relates Ppt Download


Pv Diagrams Part 2 Isothermal Isometric Adiabatic Processes Video Khan Academy
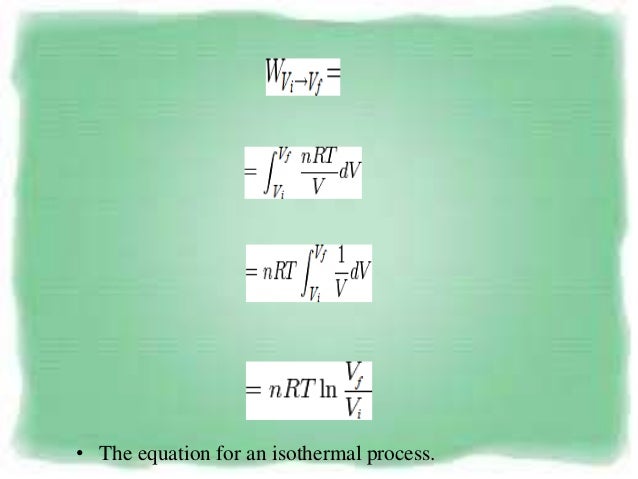


Pvt Behaviour Of Gases And Relations



Mman2700 Formula Sheet Mman2700 Thermodynamics Formula Sheet 1 Properties Of Ideal Gases P V Mrt Pv Rt P1 V1 P2 V2 T1 T2 U2 U1 Cv T2 T1 H2 H1 Course Hero



In An Adiabatic Process The State Of A Gas Is Changed From P 1
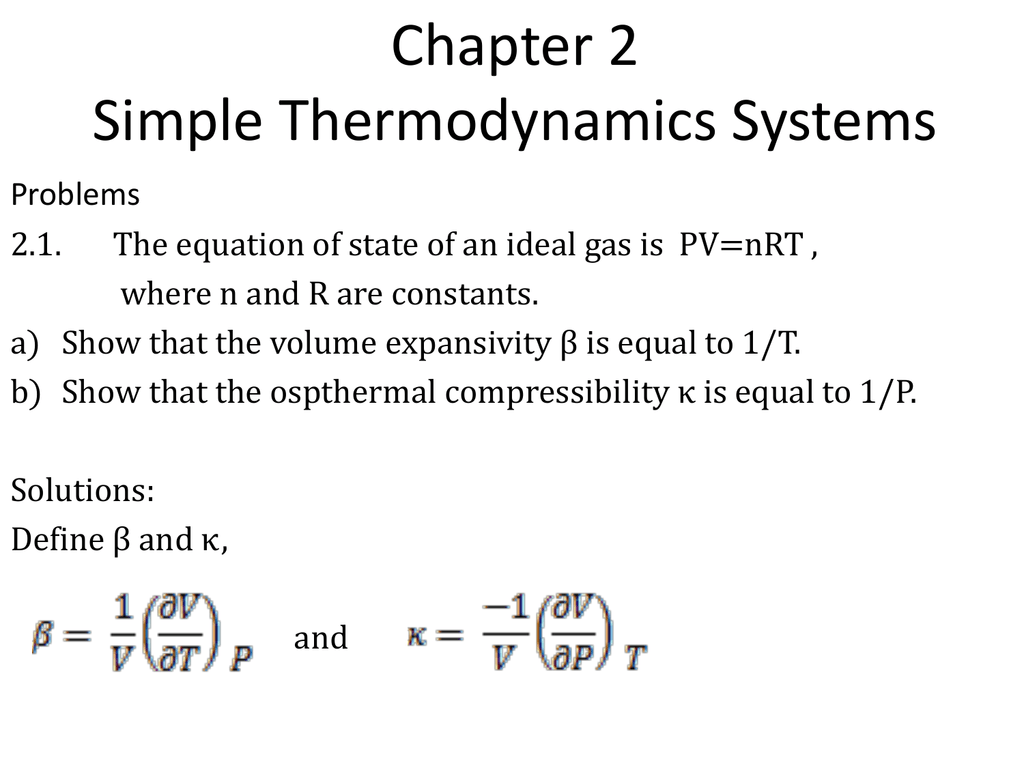


Chapter 2 Simple Thermodynamics Systems



Solutions To Homework Problem Set 10 Solar Physics At Msu



A Sketch Of Set Of Four Processes Involved In A Closed Thermodynamic System Is Shown In Homeworklib



Isentropic Process Definition Characteristics Nuclear Power Net



Adiabatic Process Relation Between P V And T Testbook



Work Done In Isothermal Vs Adiabatic Process Physics Stack Exchange



Jif 314 Thermodynamics Sidang Video 2 22 Oct



Chapter 3c The First Law Closed Systems Diesel Cycle Engines Updated 3 19 13



The First Law Of Thermodynamics And Some Simple Processes Physics



Adiabatic Process P V T Relation Youtube



Pvt Behaviour Of Gases And Relations



Adiabatic Process Relation Between P V And T Testbook
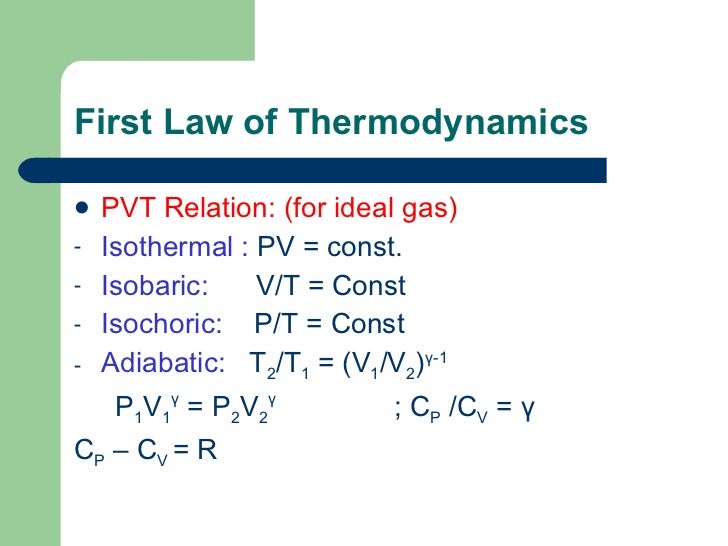


Revision On Thermodynamics



Thermodynamic Properties W Property Table From Direct Measurement
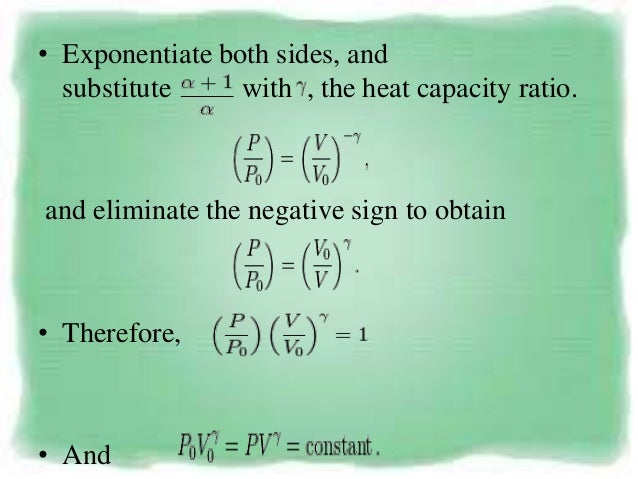


Pvt Behaviour Of Gases And Relations



Proof Of Pressure Volume And Temperature Ratio Adiabatic Process Youtube



Adiabatic Process And Applications Of Adiabatic Process Iit Jee And Neet Physics



In An Adiabatic Change The Pressure And Temperature Of A Monoatomic Gas Are Related With Relation Youtube


Adiabatic Processes For An Ideal Gas University Physics Volume 2



Obtain The Relation A P V B V T C P T During Adiaba Scholr



Thermodynamic Property Relations



Pptx Thermodynamic Applied And Interdisciplinary Physics Continuum Mechanics



Thermodynamic Relationship An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
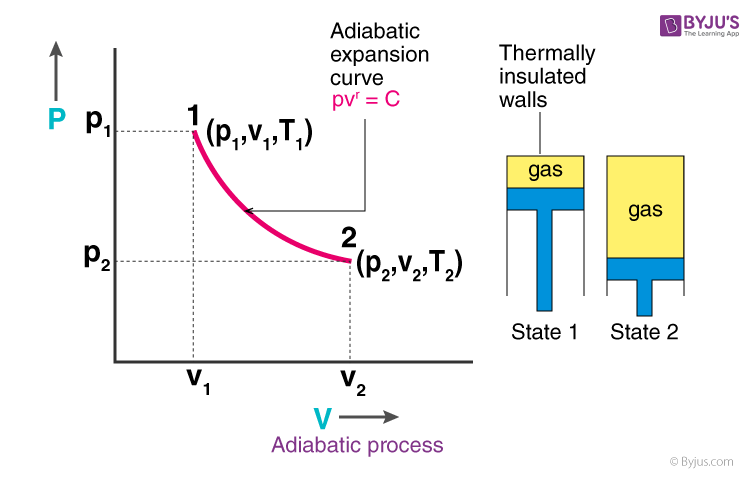


What Is Adiabatic Process Equation Reversible Diagram Example



Derivation Of Expression For Work Done In Adiabatic Process Youtube



Thermodynamic Processes And Equations
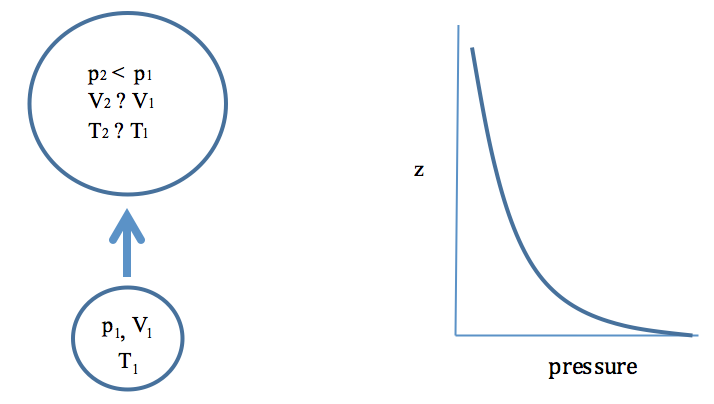


2 5 Adiabatic Processes The Path Of Least Resistance Meteo 300 Fundamentals Of Atmospheric Science
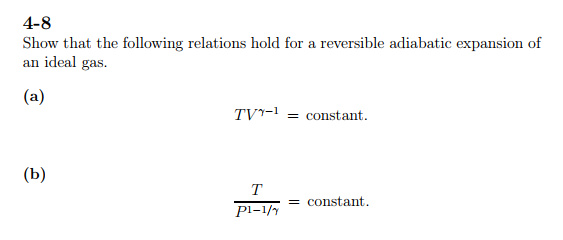


Solved 4 8 Show That The Following Relations Hold For A R Chegg Com


Solved Example Problems For Adiabatic Process Thermodynamics


Derive The Relationship Between Pressure And Volume In Adiabatic Change Quora


How To Show That For The Adiabatic Expansion Of An Ideal Gas Pv Constant Quora



Hindi Laws Of Thermodynamics And Applications By Shubham Kumar Unacademy Plus


Adiabatic Processes



Example 7e 2 Pvt Relationships For Isentropic Ig Processes



Department Of Mechanical Engineering Me 322 Mechanical Engineering



Chapter7 Lesson E Pvt Relationships For Isentropic Ig Processes



Adiabatic Process Relation Between P V And T Testbook



271f10l12 Physics Labs



Adiabatic Process And Applications Of Adiabatic Process Iit Jee And Neet Physics
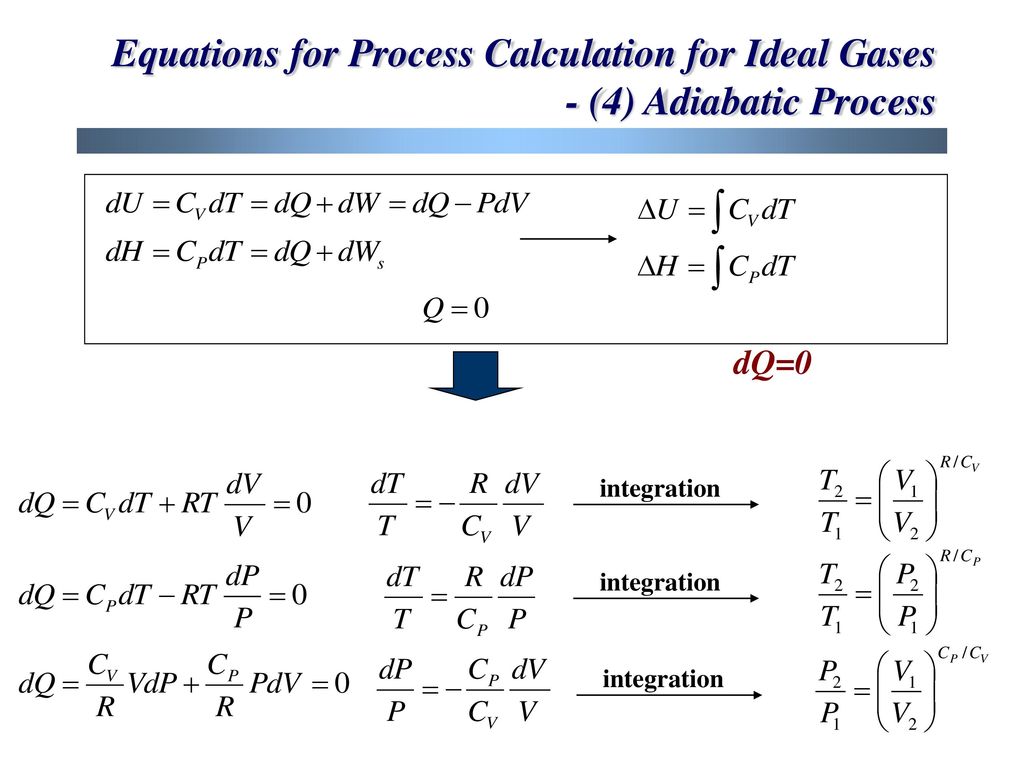


공정 열역학 Chapter 3 Volumetric Properties Of Pure Fluids Part 2 Ppt Download



The Adiabatic Process Q 0 Updated 8 25 09



Adiabatic Process And Applications Of Adiabatic Process Iit Jee And Neet Physics



An Ideal Gas Expands From Volume V1 To V2 This May Be Achieved By Either Of Three Processes Isobaric Isothermal And Adiabatic Let D U Be The Change In Internal Energy



Adiabatic Process Relation Between P V And T Testbook
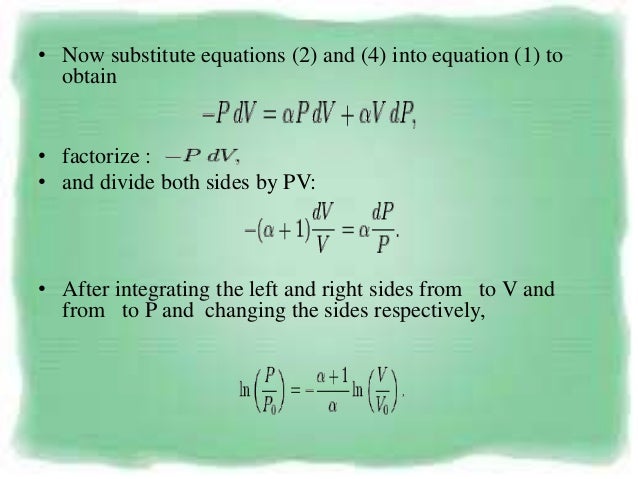


Pvt Behaviour Of Gases And Relations



Chapter 2 The First Law Of Thermodynamics For Closed Systems Thermodynamics



Shortcuts To Convert P V Diagram Into T S Diagram Exergic


コメント
コメントを投稿